New Zealand geothermal CO2 reinjection research receives government funding
A research project on CO2 reinjection in geothermal power facilities in New Zealand has received $1 million in funding from the national Ministry.
A research project on CO2 reinjection in geothermal power generation facilities by GNS Science, in collaboration with Mercury NZ Ltd., has been awarded a $1,000,000 grant from the Endeavour Smart Ideas fund.
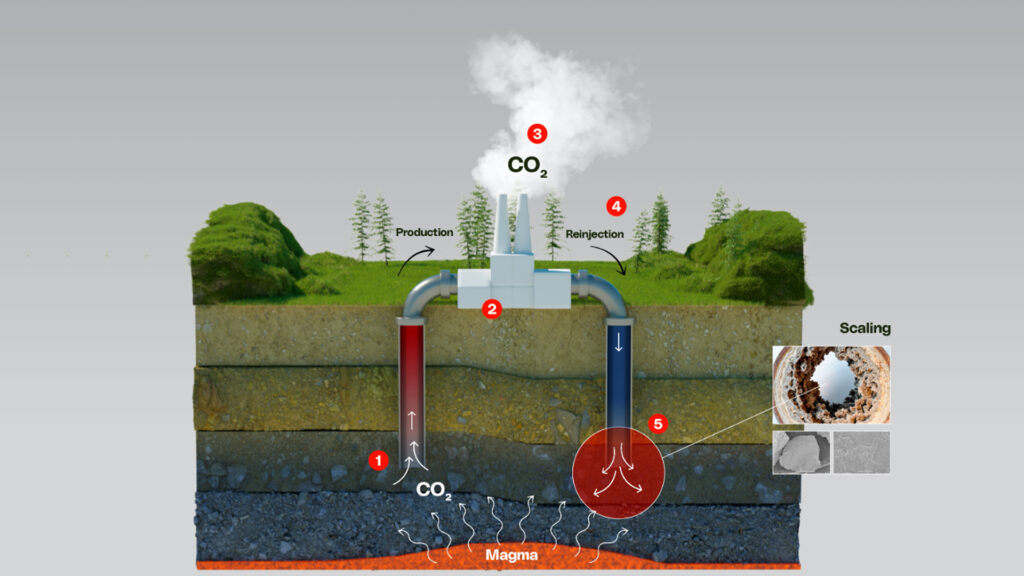
Under current practices in most parts of the world, geothermal power stations emit naturally occurring CO2 that is initially dissolved in the geothermal fluid as part of the power generation process. The operators of geothermal power plants are trialing systems that capture and reinject this CO2back underground where it came from, which stops it being released to the atmosphere.
This multi-disciplinary project aims to better understand how this reinjected CO2 affects the overall chemistry of the geothermal system and its influence on mineral scale deposition deep underground. Results of initial tests have been announced by GNS, indicating that CO2 reinjection has added benefits in terms of scaling mitigation.
Mercury had also conducted tests on CO2 capture and reinjection previously, notably at the Ngatamariki geothermal power station.
“This will help to incentivise a more rapid reduction in CO2 emissions across the sector, as well as allowing geothermal plants to operate more efficiently,” said Dr David Byrne, Project Lead at GNS Science. “Through this research we aim to demonstrate the efficacy of CO2 reinjection and develop a toolset that will allow operators to understand its long-term effects on their geothermal reservoirs.”
Managed by the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment, the Endeavour Smart Ideas fund aims to catalyze the testing and progress of innovative, ambitious, and well-defined research ideas that have high potential to benefit New Zealand across a range of economic, environmental, and societal objectives.
Source: GNS Science



















